
Principle and significance
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a molecular biology technique used to amplify specific DNA fragments in vitro, similar to the natural replication process of DNA. The five elements involved in the reaction of PCR experiments include template DNA, primers, 4 kinds of deoxynucleotides, DNA polymerase and Mg2+, and the DNA fragment to be amplified and the oligonucleotide strand primers complementary on both sides undergo multiple cycles of the three-step reaction of "high temperature denaturation - low temperature annealing - primer extension", so that the number of DNA fragments increases exponentially, so as to obtain a large number of specific gene fragments we need in a short time.
PCR technology was established in 1983 by Kary Mullis of PE Cetus in the United States, for which he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1993. This technology can amplify specific DNA fragments in a test tube millions of times in a matter of hours, and this technology for rapidly obtaining a large number of single nucleic acid fragments is of great significance in the field of molecular biology research, which greatly promotes the progress of life science research. Moreover, it is not only the most commonly used technology for DNA analysis, but also has important application value in DNA recombination and expression, gene structure analysis and functional detection.

Denaturation of template DNA: The copied DNA fragment is heated under conditions higher than its Tm (93~95 °C), so that the hydrogen bond of the DNA double helix structure is broken by the second helix, forming two single-stranded molecules as templates for the amplification reaction in order to bind to the primers and prepare for the next round of reaction.
Annealing of template DNA and primers: This step, also known as renaturation, reduces the temperature of the reaction system to below the melting point temperature of oligonucleotides (primers) (40~70 °C) so that the primers can be complementary and paired with the template DNA sequence to form a hybrid strand.
Primer extension: the temperature of the reaction system is raised to about 72 °C, at this time the reaction system takes dNTP as the reaction raw material, the target sequence as the template and according to the principle of base complementary pairing and semi-preserved replication, under the action of Taq DNA polymerase, the hybridization strand continues to extend until a new DNA double strand is formed, and this new strand can be called the template of the next cycle.
It takes 2~4 minutes to complete each cycle, and 2~3 hours can amplify the gene to be expanded millions of times.
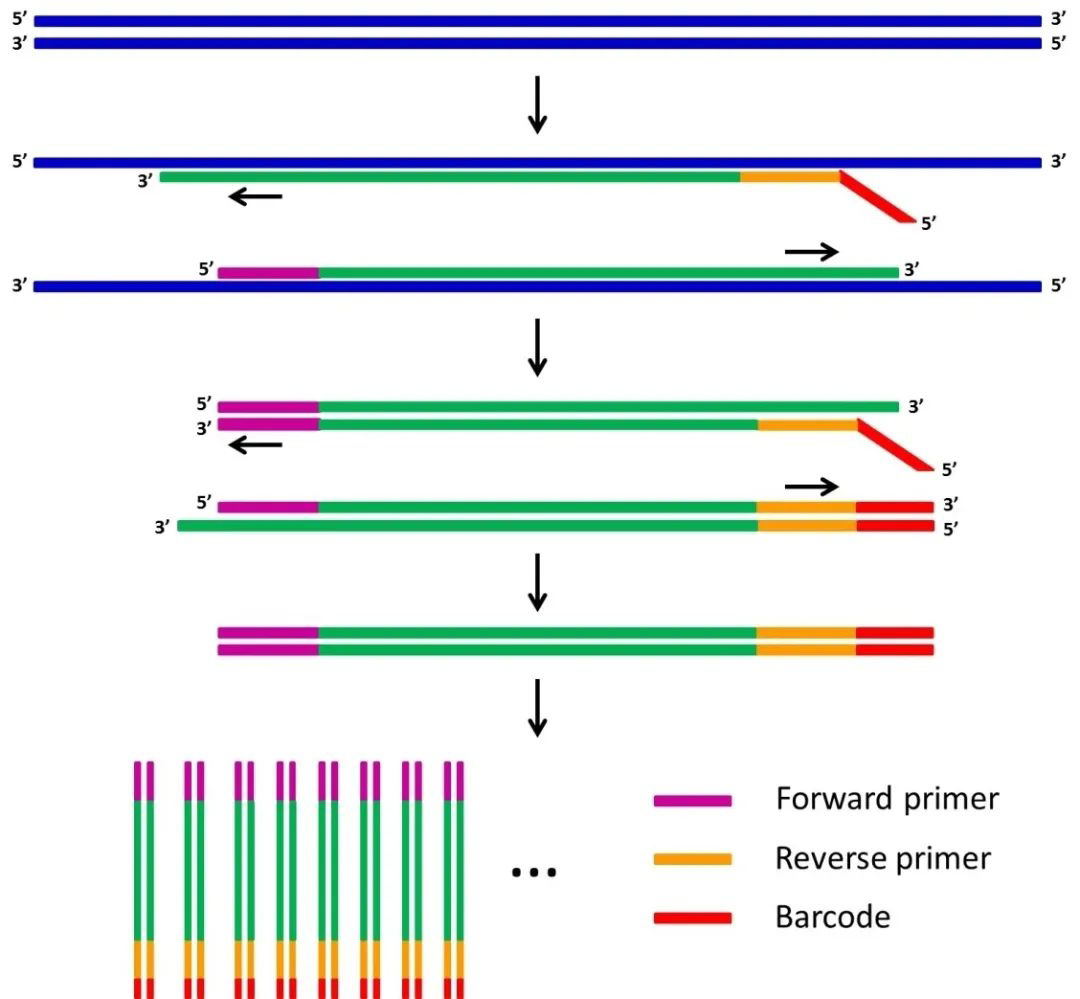
Based on PCR, related technologies commonly used in various experimental studies include reverse transcription PCR, single-cell PCR, PCR-induced fixed-point mutation, in situ PCR, quantitative PCR and digital PCR. After nearly 30 years of development, PCR technology has been widely used in various basic research and clinical laboratory diagnosis, such as the laboratory departments of some hospitals have also begun to standardize real-time fluorescent PCR detection projects to provide further disease monitoring and prognosis for patient treatment. The author has also used quantitative fluorescence PCR to determine the expression of a specific anti-Verticillium wilt gene in the root of the susceptible material 'Olecra longicorn' at different times after infection with Rotissellium dahlia.

Planning and production
Planner: Rongda Bio Marketing Department | Cover image source: Rongda Biodesign Team